How Are Xylem And Phloem Adapted To Their Function
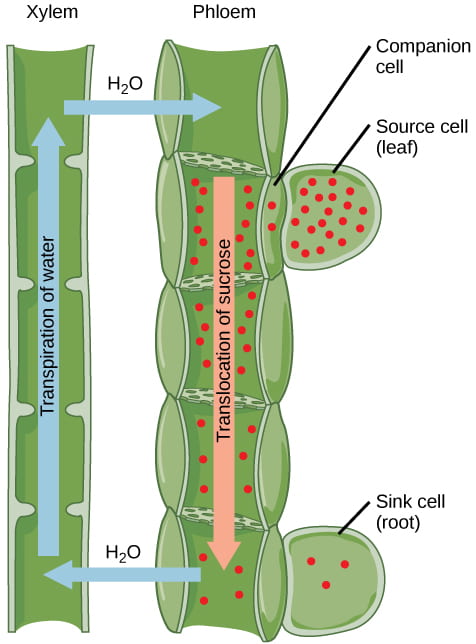
In xylem vessels water travels by bulk flow rather than cell diffusionIn phloem concentration of organic substance inside a phloem cell eg leaf creates a diffusion gradient by which water flows into cells and phloem sap moves from source of organic substance to sugar sinks by turgor pressure. Whereas phloem carries the food prepared by the leaves to different parts of the plant.
What Is Xylem And Its Function Quora
The phloem is towards the centre outside the xylem.
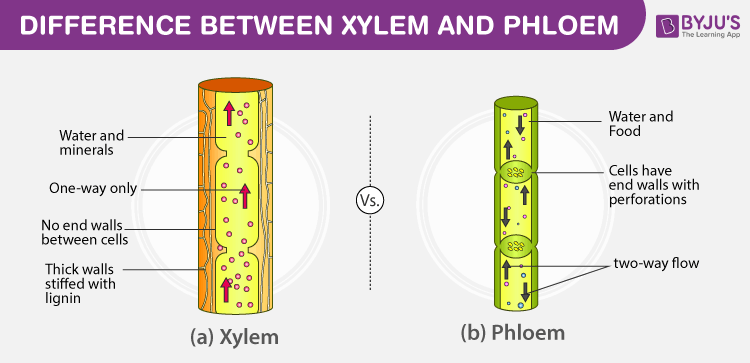
How are xylem and phloem adapted to their function. They lose their end walls so the xylem forms a continuous hollow tube. These systems use continuous tubes called xylem and phloem. There are two organs involved in transporting of materials in plants ie.
They lose their end walls so the xylem forms a continuous hollow tube. Unlike xylem which is composed primarily of dead cells the phloem is composed of still-living cells that transport sap. Xylem carries water and minerals from the roots to the leaves.
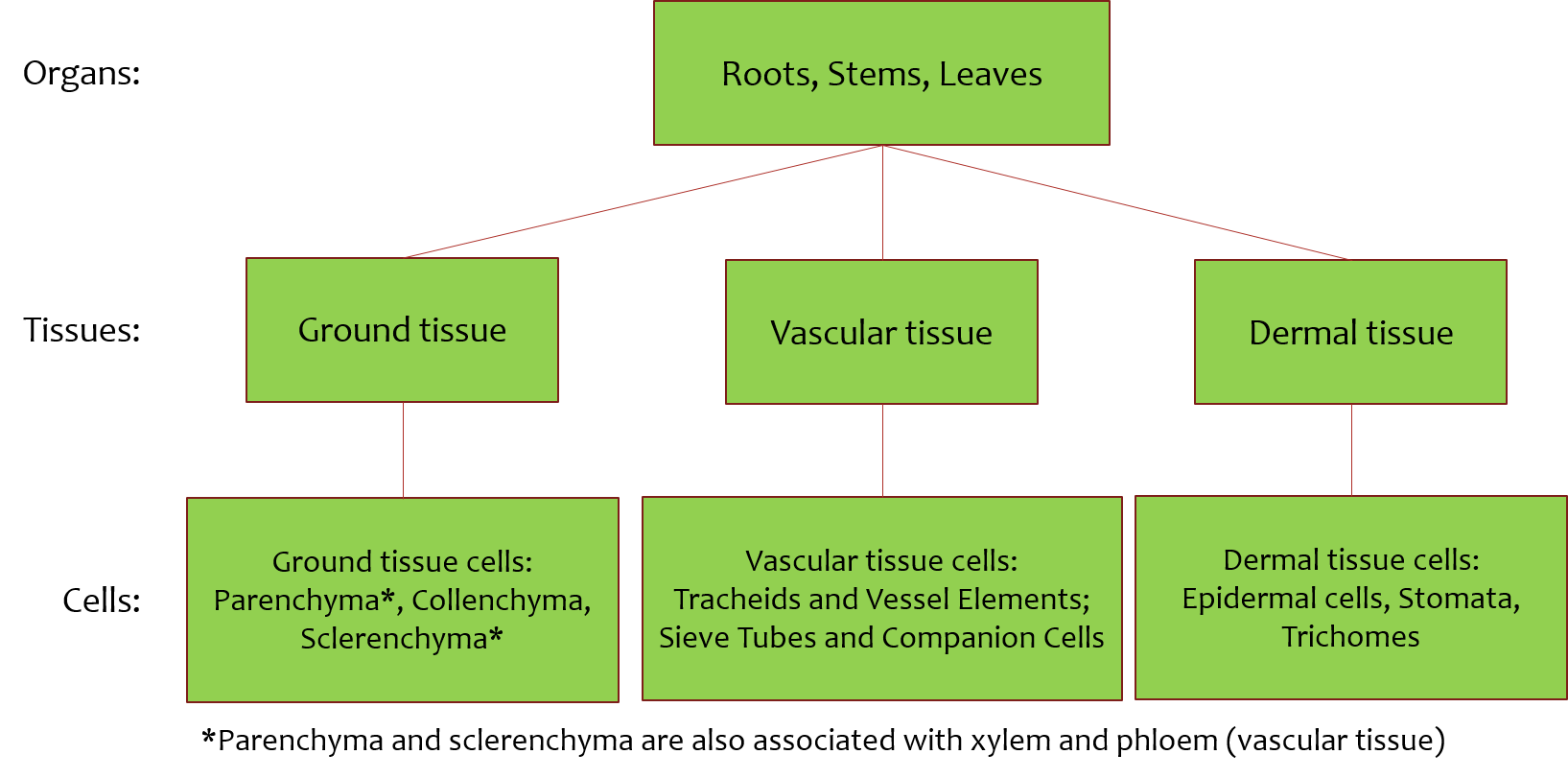
The cells that make up the xylem are adapted to their function. Lignin gives strength and support to the plant. The xylem and the phloem.
Are xylem cells dead. Plants have transport systems to move food water and minerals around. Xylem and phloem facilitate the transportation of water minerals and food throughout the plant.
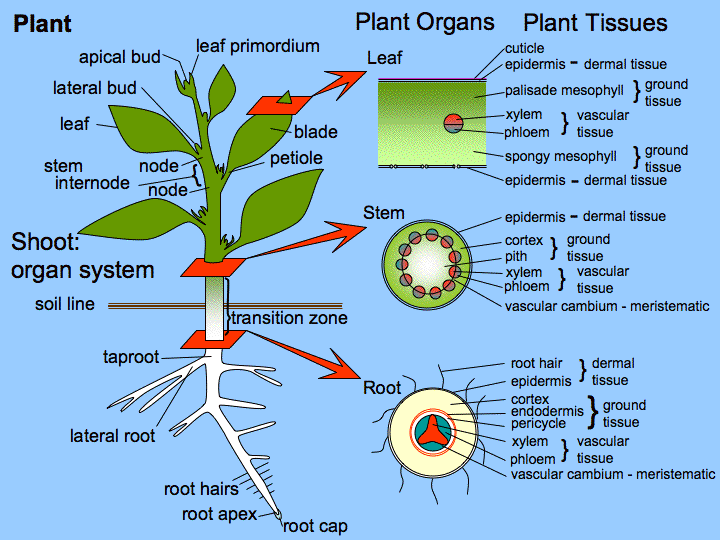
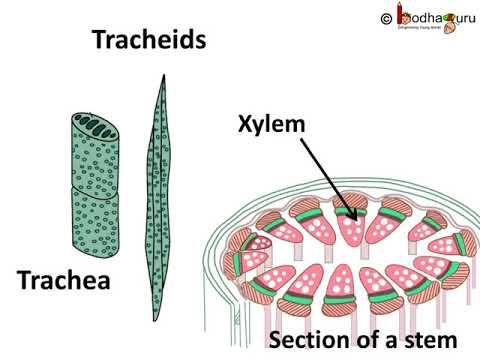
Xylem carries water and minerals from the roots to the leaves. These sugars are transported to non-photosynthetic parts of the plant such as the roots or into storage structures such as tubers. How are xylem and phloem arranged in stems In the stems the xylem and phloem are near the outside to provide a sort of scaffolding that reduces bending.
Whereas phloem carries the food prepared by the leaves to different parts of the plant. They become strengthened by a substance called lignin. They become strengthened by a substance called lignin.
Xylem moves water from roots to the leaves and phloem moves food from the leaves to the rest of the plant. Xylem vessels are made up of hollow cells designed to carry water and minerals from the roots of a plant to the trunk with altered cell walls to allow for the passage of one vessel to another. Xylem tissue is used mostly for transporting water from roots to stems and leaves.
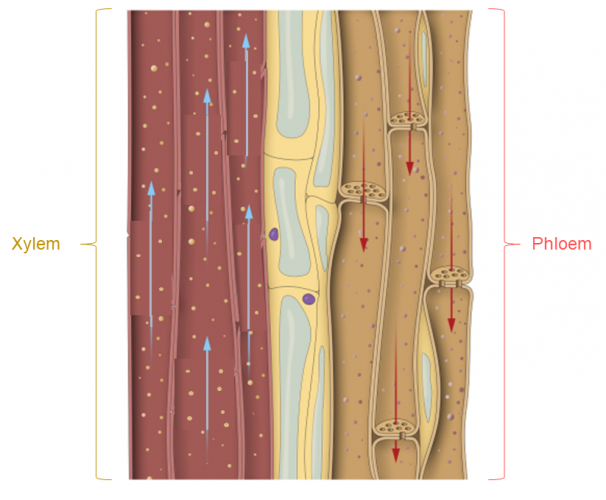
In the root the xylem forms a central column forming a solid support. They become strengthened by a substance called lignin. Xylem and phloem adaptations.
THE XYLEM Function The xylem transports water and dissolved mineral salts Structure Xylem is a compound tissue consisting of different types of cells. The most important ones are the xylem. How are xylem and phloem arranged in roots In a root the xylem is in the centre surrounded by the phloem to provide support for the root as it pushes through the soil.
They lose their end walls so the xylem forms a continuous hollow tube. They also provide structural support to vascular plants. - Xylem vessels carry water and minerals from the roots to the leaves - Phloem tubes carry sugar other organic nutrients made by plant from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
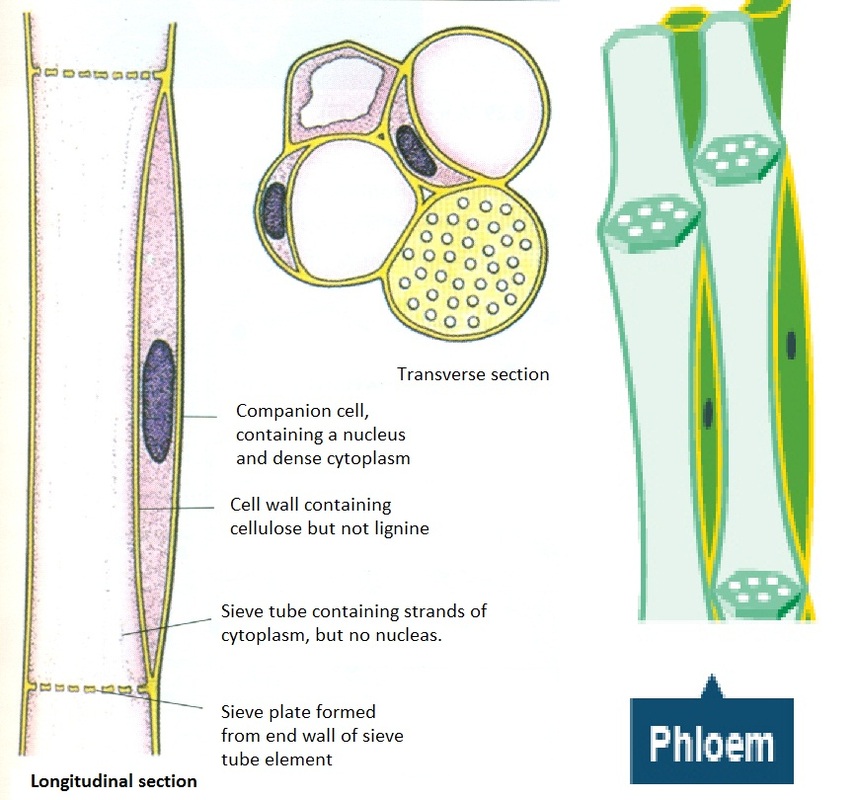
Each sieve tube has a perforated end so its cytoplasm connects one. The xylem and phloem are distributed differently in roots and stems. Sieve tubes specialised for transport and have no nuclei.
The cells that make up the xylem are adapted to their function. Terms in this set 2 Xylem water an dissolved minerals Made from dead cells aligned end to end to form a continuous tube Tubes are narrow so water column doesnt break easily and capillary action is effective. Both phloem and xylem are tubular structures that facilitate easy transportation.
One xylem and one phloem are known as a vascular bundle and most plants have multiple vascular bundles running the length of their leaves stems and roots. Xylem and phloem facilitate the transportation of water minerals and food throughout the plant. The cells that make up the xylem are adapted to their function.
The cells that make up the phloem are adapted to their function. During transpiration water evaporates from the leaves and draws water from the roots.

Xylem And Phloem A Level The Science Hive

Stem T S Epidermis Using The Diagram Above State The Function Of Each Of The Following Tissues 10mins Cortex Cambium Epidermis Root Cap Xylem Phloem Ppt Video Online Download

25 4b Vascular Tissue Xylem And Phloem Biology Libretexts

Xylem Phloem Communication Network Control Over Nitrogen Fixation In Download Scientific Diagram
Analyse The Roles Of Xylem And Phloem In Plants Worksheet Edplace

Module 3 1 Transport In Plants Xylem And Phloem Diagram Quizlet
Water Transport In Plants Xylem Organismal Biology
Label And Annotate The Phloem Xylem And

Difference Between Xylem And Phloem Major Differences
Functions Of Xylem And Phloem Biology Notes For Igcse 2014
Sugar Transport In Plants Phloem Organismal Biology

Ap Biology For Dummies Phloem Xylem
Plant Development I Tissue Differentiation And Function Organismal Biology

Vascular Tissue Xylem And Phloem Ppt Video Online Download
Plant Development I Tissue Differentiation And Function Organismal Biology



Post a Comment for "How Are Xylem And Phloem Adapted To Their Function"